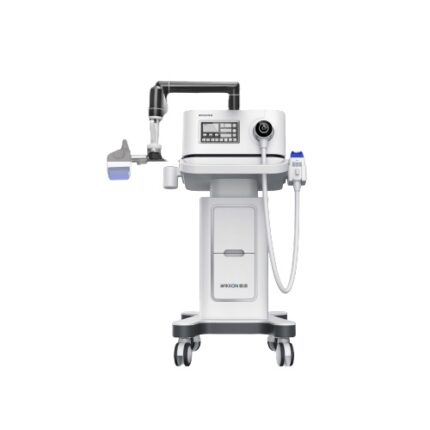
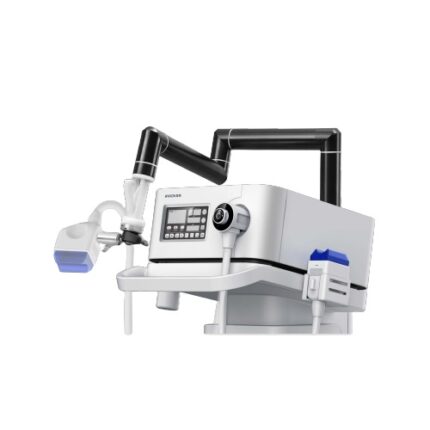
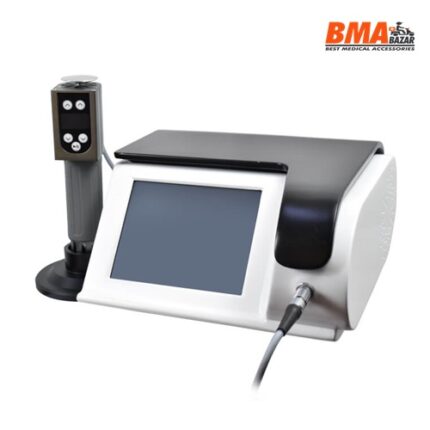
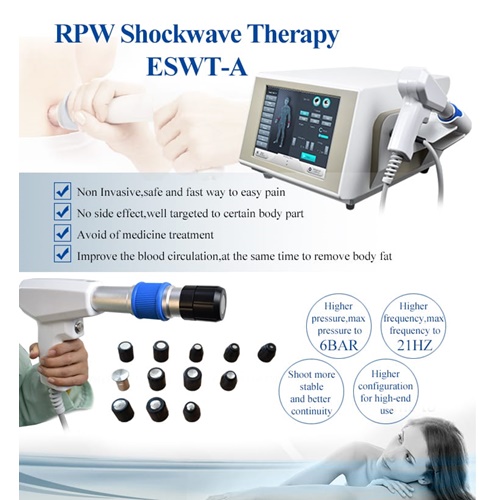
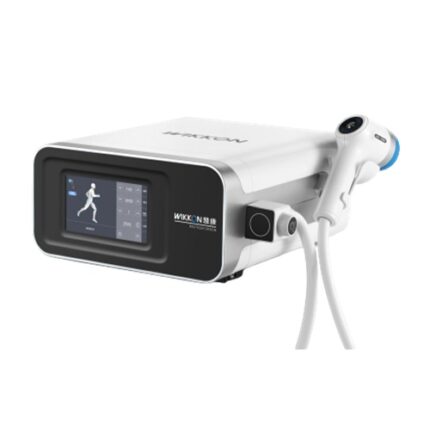
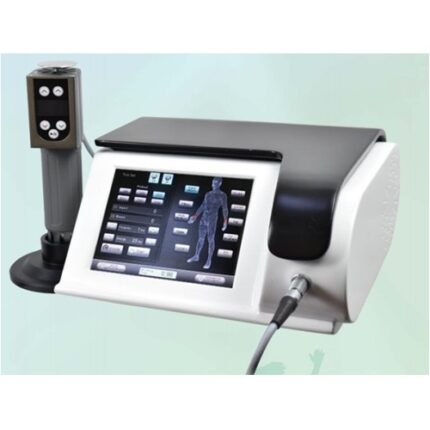
Description
A shockwave is defined as a wave with a rapid increase of pressure within a very short time and then having a gradual decrease of pressure with a small negative pressure phase. Shockwave is aimed at the affected areas that are the source of chronic pain. The influence of the shockwaves causes to the dissolution of calcium deposits and leads to better vascularization. The after-effect is relief from the pain.
Advantages
- High quality, fast pain relief.
- Noninvasive, no anesthetic, simple and convenient
- Just 20 minutes per nursing, 5-10 per session nursing.
- Widely applicable to treatments of various soft tissues
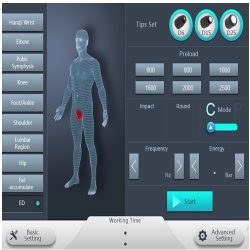
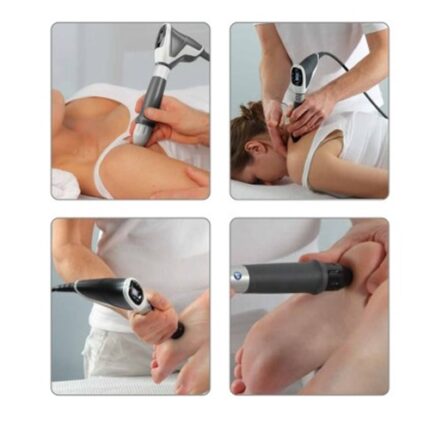
Treatment
- Elbow of tennis Painful tendon connection inflammation in the lateral elbow
- With or without calcification, shoulder pain Painful restriction of movement of the shoulder
- Elbow of the Golfer Painful inflammation of the connection of the tendons to the medial elbow
- Trochanteric Bursitis Painful hip periostitis
- Syndrome with Patella tip Tibial edge inflammation as a result of prolonged pressure
- Syndrome of the tibial edge inflammation as a result of prolonged pressure
- Akhillodynia Painful Achilles tendon irritation
- And a sore heel Painful, mainly chronic heel inflammation
- Inflammation of the binding of a tendon Due to overexertion or improper pressure, or due to degenerative processes, painful inflammation of tendon attachments
- Points for Acupuncture Via acupuncture care, pain therapy points to
- Painful points for the cause Acute and persistent pain due to chronically shortened and thickened muscles in the back, leg, neck, etc.
Benefits
Physical effects of Radial Pressure Waves offer a noninvasive treatment solution for long term insertion and soft tissue pathologies. Local treatment of the affected area will enhance and reset the healing pattern. Today there are several working hypotheses for the physical effects of radial pressure waves:
- Shockwaves create increased cell membrane permeability metabolically which allows old, damaged, and weakened cells to be removed and replaced with healthy viable cells.
- And neurologically, Shockwaves produce a counter-irritation at the dorsal root ganglion actually modulating the amount of nociceptive activity and decreasing the pain signal, and actually closing the theoretical pain gate.
- Vascular changes such as increased blood circulation in tissues increase the oxygen content and significantly reduces the concentration of carbon dioxide in the tissue which may stimulate the healing process.
- Based on the hypothesis towards associative pain memory (Wess), afferent pain signals are transmitted through the central nervous system by multiple synaptic junctions which eventually cause efferent fibers to control muscle tone. The reflex mechanism



























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.